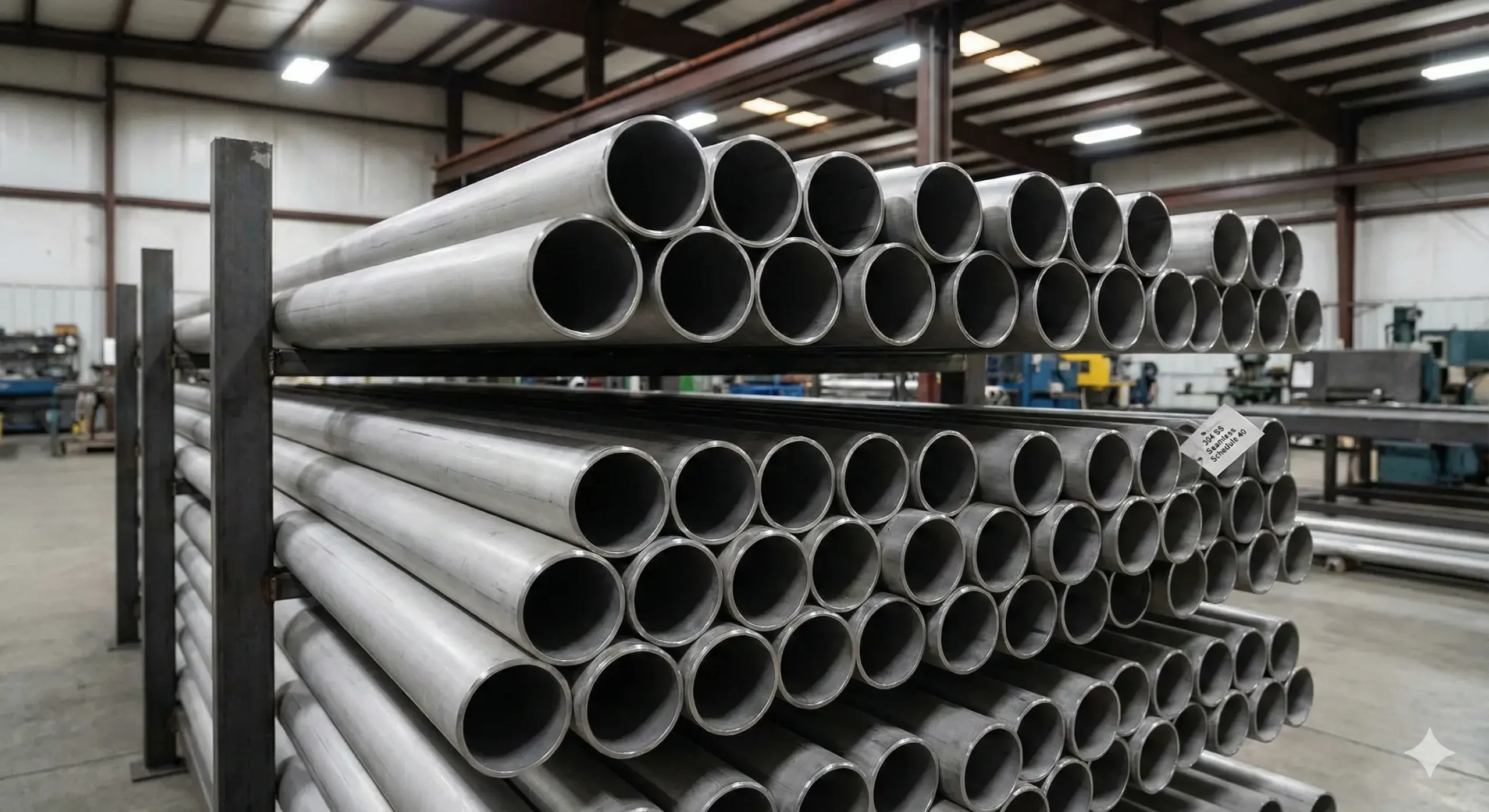

Confused by seamless pipes and welded pipes? Many buyers are. The wrong choice could mean higher costs or safety risks.
304 stainless steel seamless pipes are made from solid billets without welds, offering superior strength, corrosion resistance, and pressure performance.
This guide explains how they're made, why they matter, and how to use them effectively.
What Are Stainless Steel 304 Seamless Pipes?
Unfamiliar with what makes a pipe "seamless"? You're not alone.
304 stainless steel seamless pipes are hollow tubes made without welding, using solid steel billets formed into cylinders.
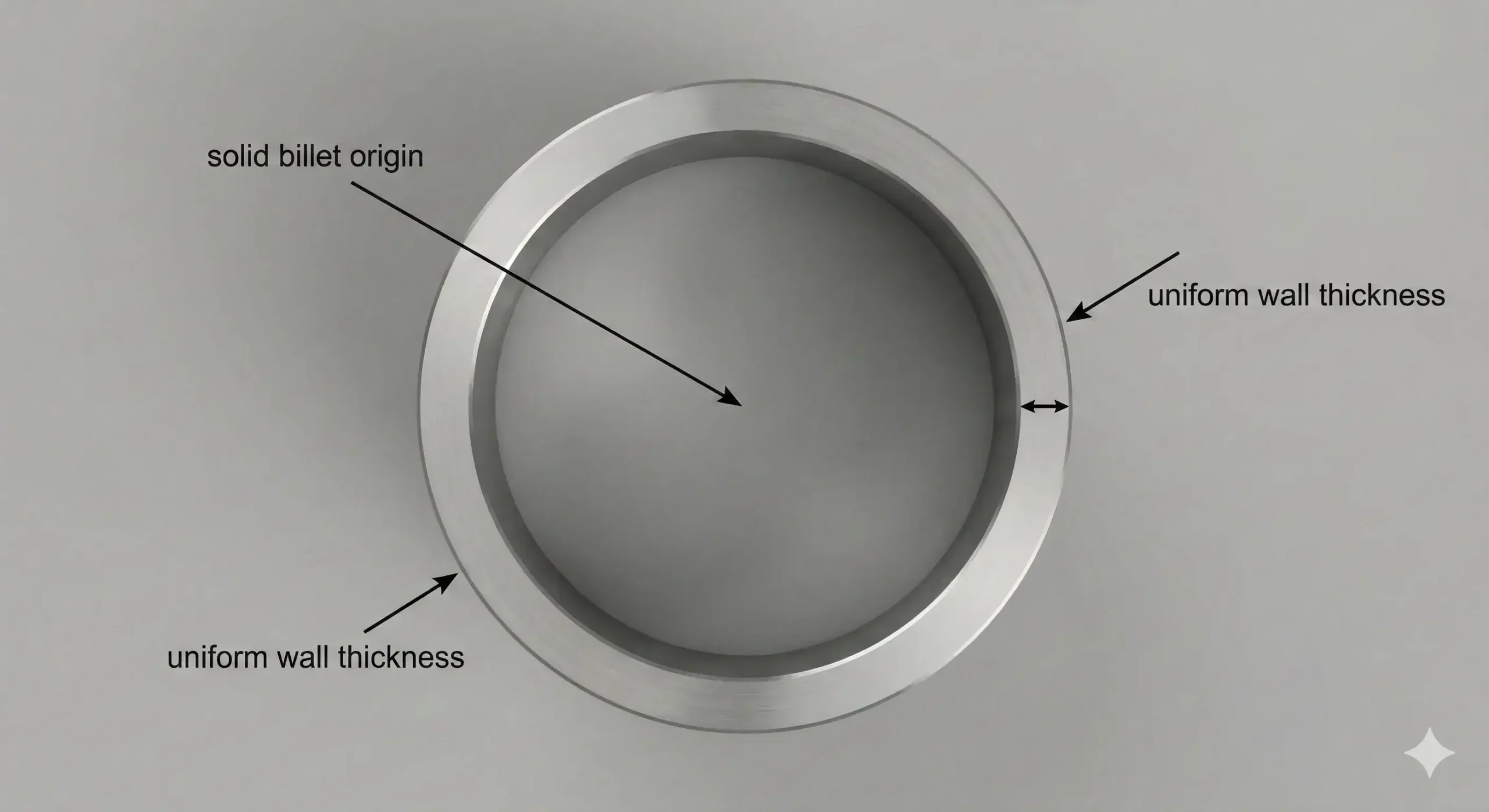
How They're Built Differently
Most pipes are welded—two pieces joined at the seam. Seamless pipes are stronger and leak-resistant because they have no seams.
| Feature | 304 Seamless Pipes |
|---|---|
| Welds | None |
| Strength | High |
| Pressure Resistance | Excellent |
| Common Use | High-purity and high-pressure systems |
Seamless means fewer weak spots and fewer failures.
How Are 304 Stainless Steel Seamless Pipes Manufactured?
Wondering how seamless pipes come to life?
They are made by heating a stainless steel billet and piercing it into a tube without welding.
Process Overview
-
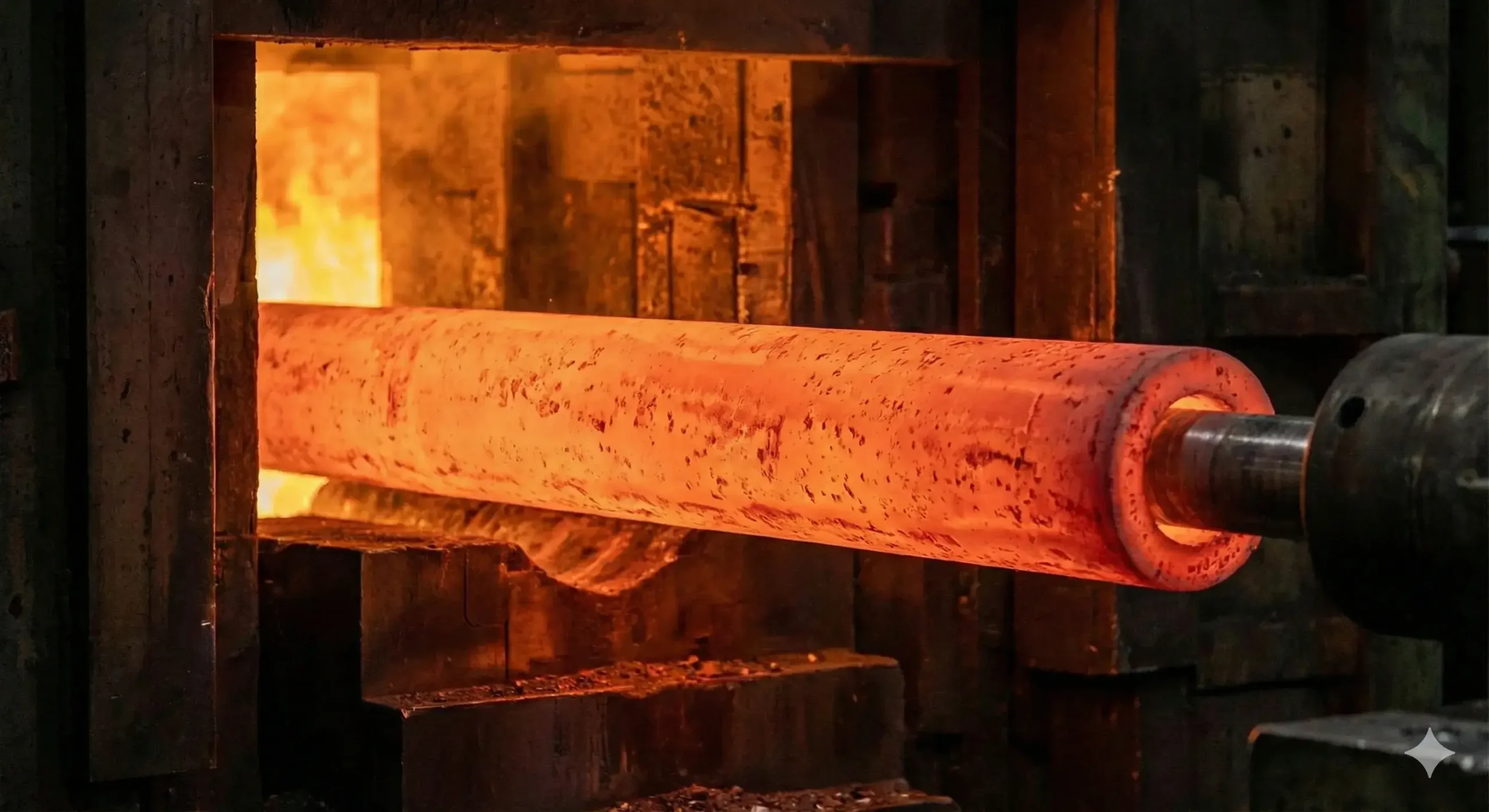
Step 1: Start with a solid 304 stainless steel billet

-
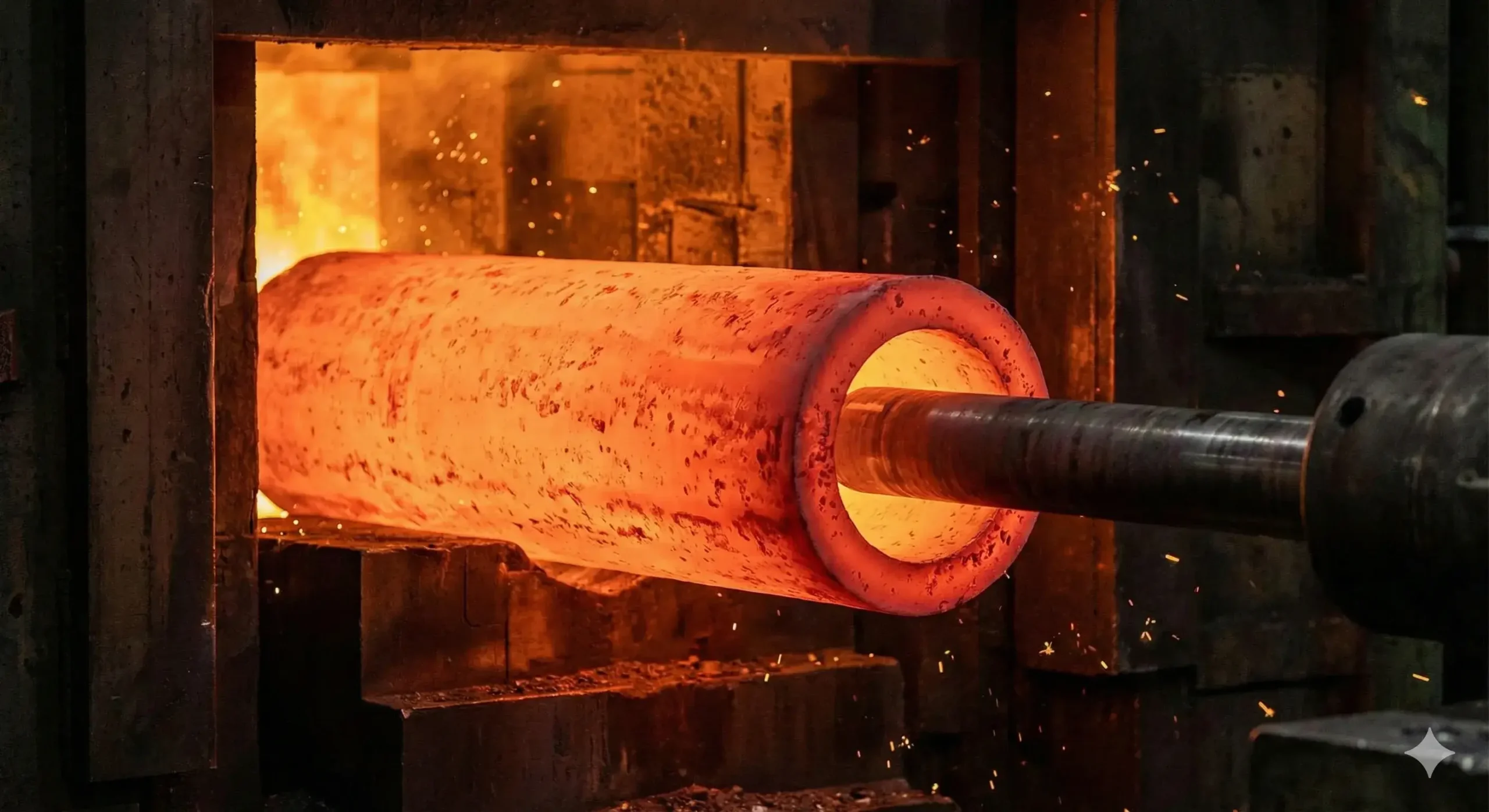
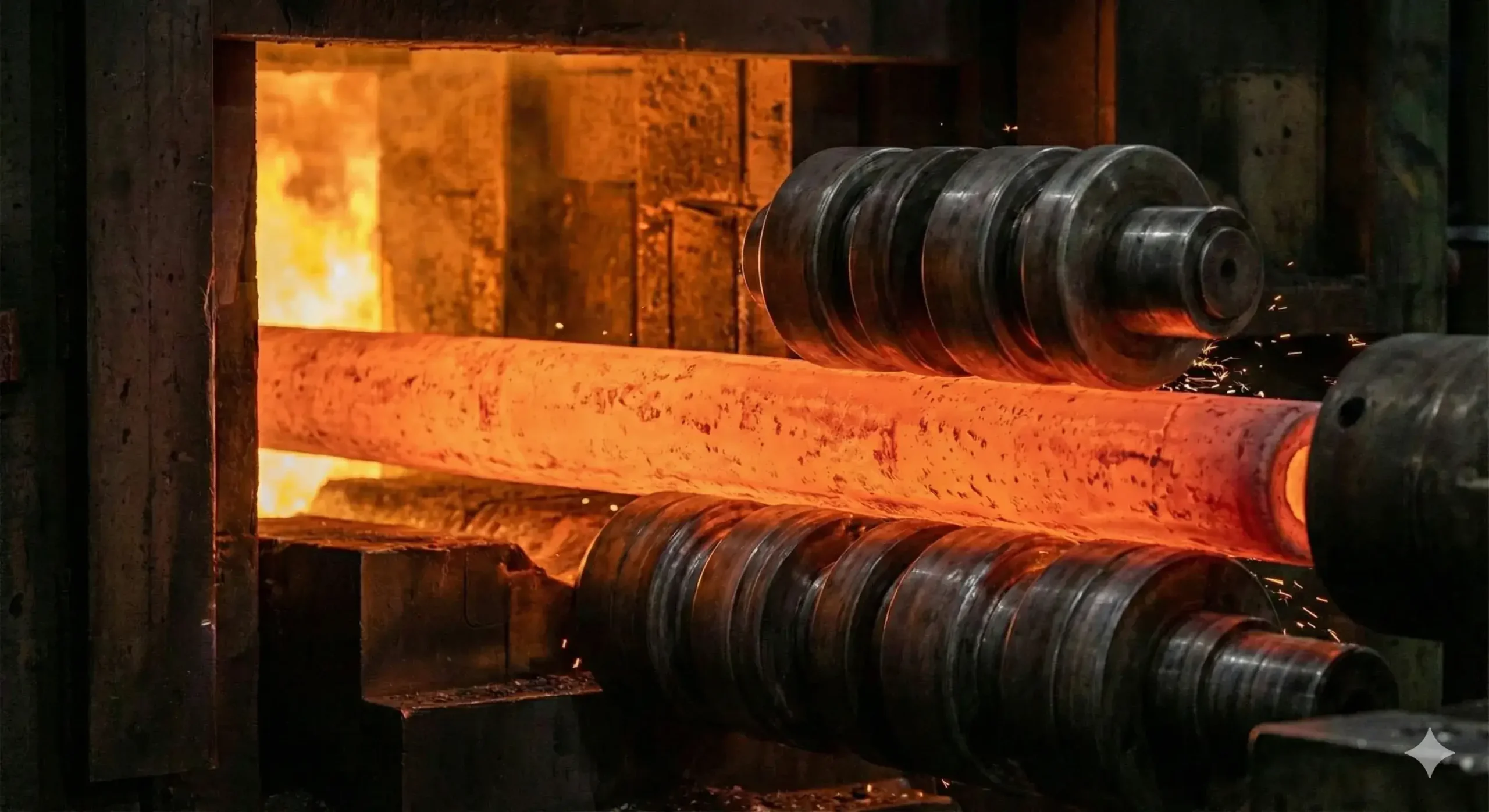
Step 2: Heat and pierce using extrusion or rotary piercing process1

-
Step 3: Roll and stretch to size

-
Step 4: Heat treat and surface finish

Because there's no seam, the wall thickness stays uniform, ensuring consistent strength.
What Is the Chemical Composition of 304 Stainless Steel Seamless Pipes?
Materials matter. 304 stainless steel is built for reliability.
304 seamless pipes contain 18-20% chromium and 8-10.5% nickel, with carbon limited to 0.08%.
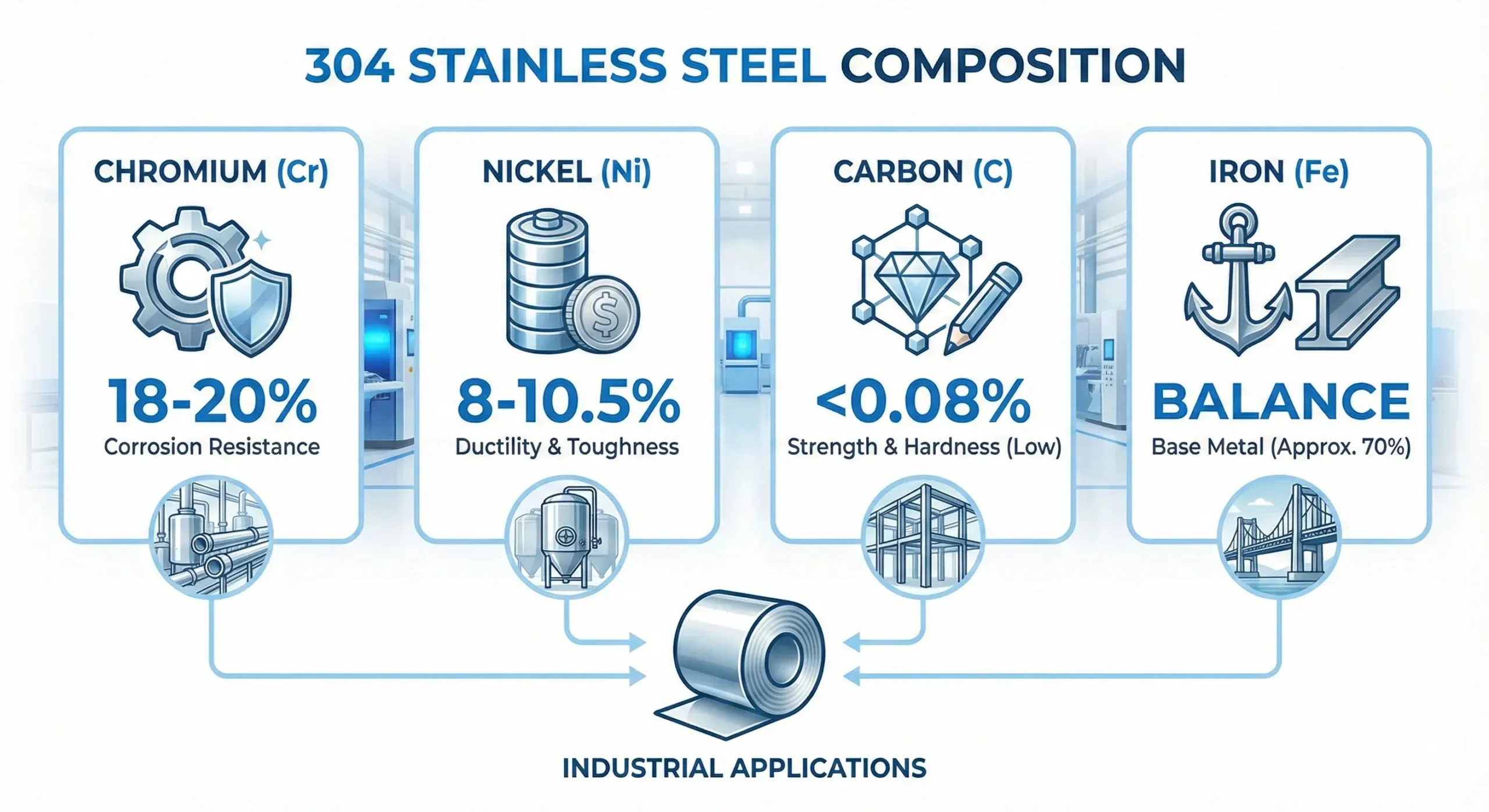
Element Breakdown
| Element | Range | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Chromium | 18–20% | Forms protective chromium oxide layer2 |
| Nickel | 8–10.5% | Ductility and formability |
| Carbon | ≤ 0.08% | Limits carbide precipitation |
| Iron | Balance | Base metal |
This austenitic stainless steel3 blend gives 304 pipes their strength and rust resistance.
What Are the Mechanical Properties of 304 Stainless Steel Seamless Pipes?
Need a pipe that can take pressure? You're in the right place.
304 seamless pipes have 205 MPa yield strength, 515 MPa tensile strength, and at least 40% elongation.
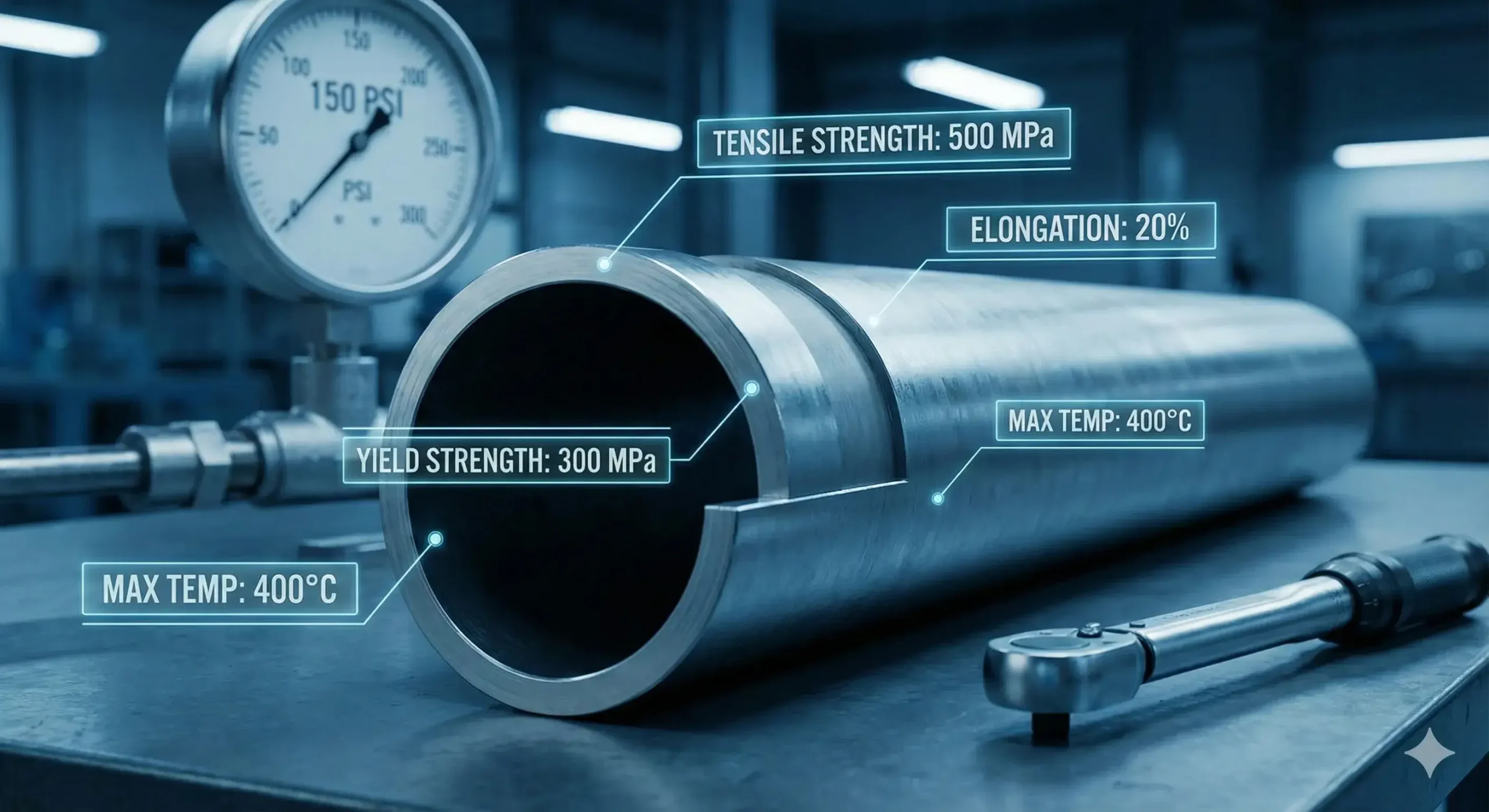
Performance Data
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Yield Strength | ≥ 205 MPa |
| Tensile Strength | ≥ 515 MPa |
| Elongation | ≥ 40% |
| Density | 8.0 g/cm³ |
| Max Operating Temp | ~870 °C |
These values meet ASTM A3124 and GB/T standards, ensuring industrial-grade durability.
What Are the Key Advantages of Using 304 Stainless Steel Seamless Pipes?
Choosing seamless means choosing reliability.
304 seamless pipes resist corrosion, handle high pressure, and ensure hygiene in critical systems.

Why Choose Seamless?
- No welds: No weak points
- Smooth finish: Sanitary surface finish5 for food and pharma
- Long lifespan: High durability, low maintenance
- Heat tolerance: Withstands up to ~870 °C
These benefits make 304 seamless pipes ideal for demanding applications.
In Which Industries Are 304 Stainless Steel Seamless Pipes Commonly Used?
Don't know where to use them? Here's where they shine.
304 seamless pipes are used in chemical, food, oil, pharmaceutical, and architectural industries.

Industry Examples
- Food & Beverage: Safe and hygienic transport of liquids
- Petrochemical: Resists harsh chemicals and pressure
- Pharmaceutical: Clean surface prevents contamination
- Architecture: Strong and weather-resistant piping
Versatility makes them valuable across many sectors.
How Do 304 Seamless Pipes Compare to Welded Pipes?
Both look the same from outside. Inside, they're not.
Seamless pipes are stronger, safer, and longer-lasting than welded pipes, which have joints prone to failure.
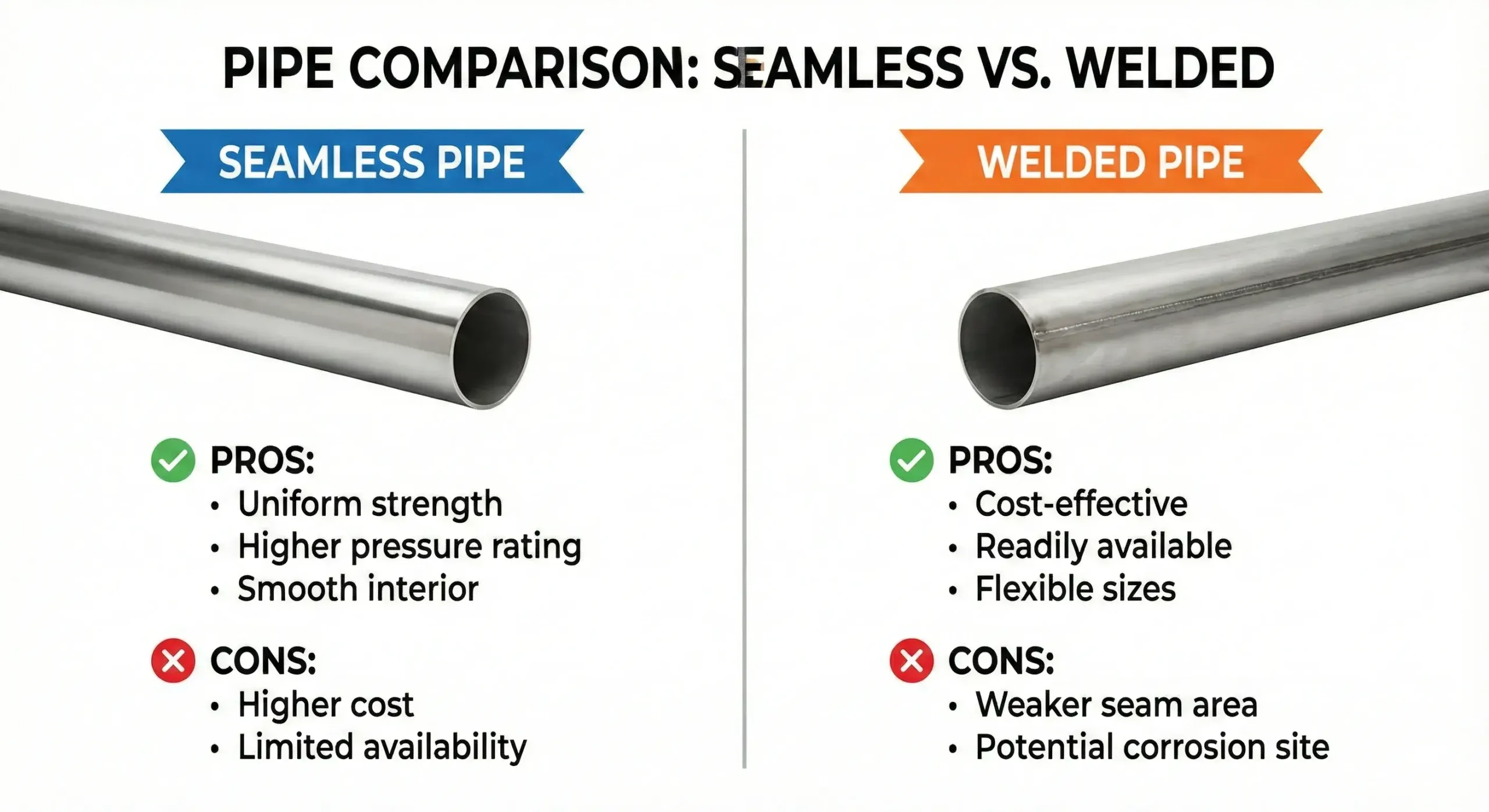
Comparison Table
| Feature | Seamless Pipe | Welded Pipe |
|---|---|---|
| Welded Joints | None | Yes (visible seam) |
| Strength | High | Lower at seams |
| Pressure Resistance | Better | Moderate |
| Price | Higher | Lower |
Use seamless when performance matters more than price.
What Are the Size and Thickness Specifications for 304 Stainless Steel Seamless Pipes?
Need specifics? Let's look at the options.
304 seamless pipes come in sizes from 1/8" to 30" in diameter with various wall thicknesses.
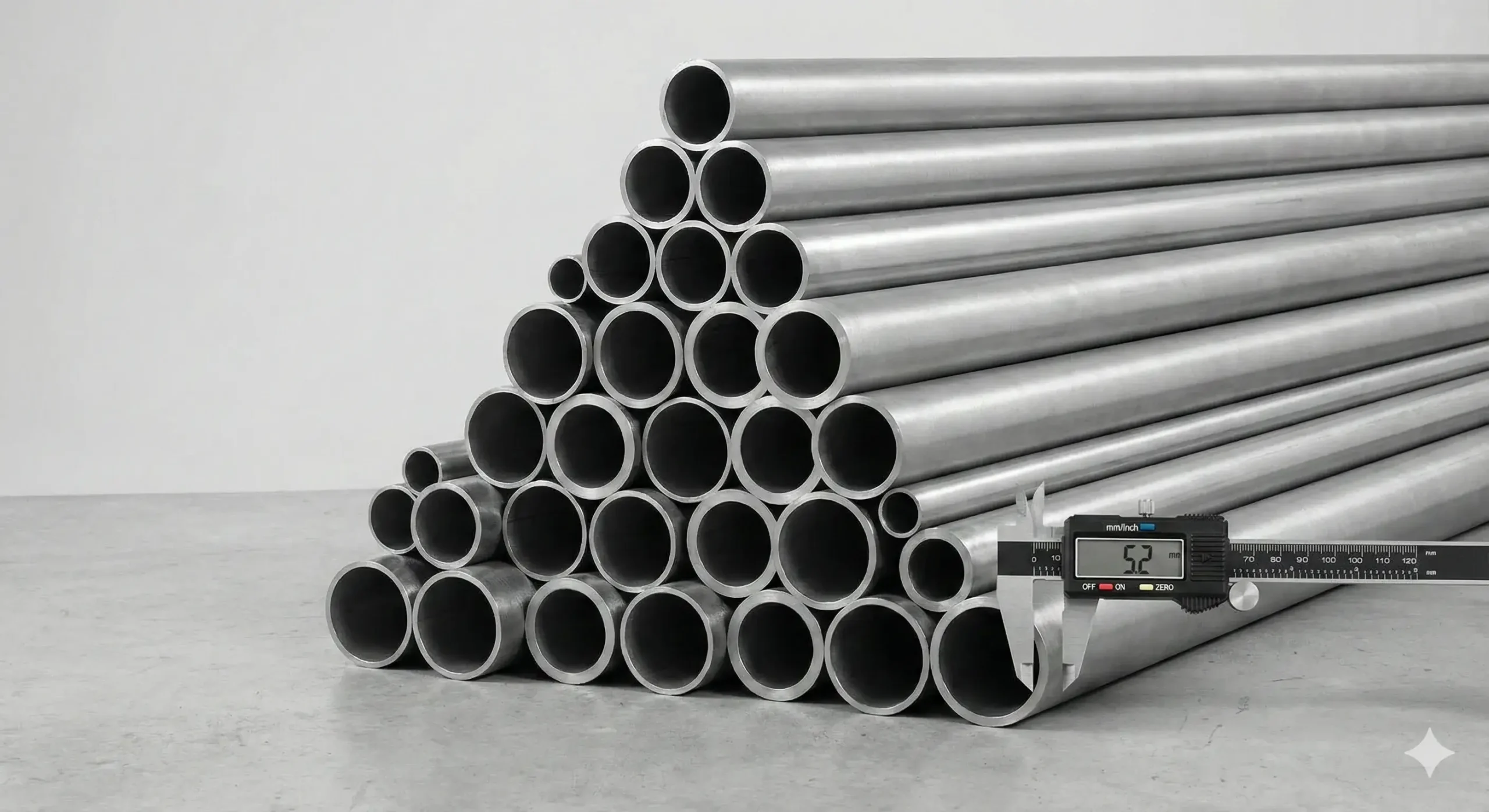

Common Schedules
| Nominal Size | Schedule 10 | Schedule 40 | Schedule 80 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1" | 0.109" | 0.133" | 0.179" |
| 2" | 0.154" | 0.154" | 0.218" |
| 4" | 0.237" | 0.237" | 0.337" |
Select based on flow rate and pressure needs.
How Does the Surface Finish of 304 Seamless Pipes Affect Their Performance?
In clean applications, finish matters.
Polished seamless pipes reduce contamination and are easier to clean.
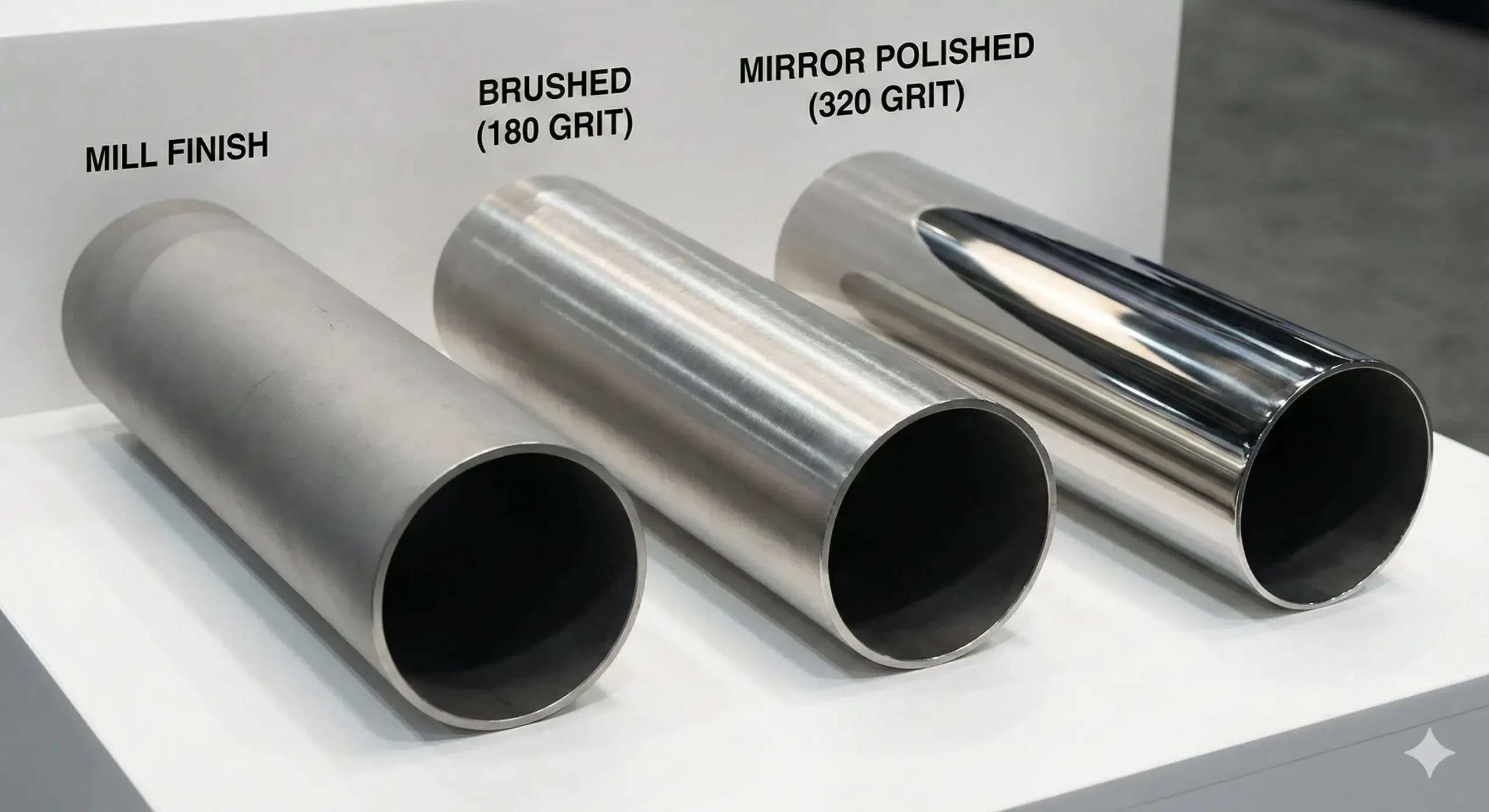

Surface Grades
- Mill Finish: Standard, unpolished
- 180 Grit Polish: Basic sanitary use
- 320 Grit Polish: Mirror finish with Ra values6 below 0.5 µm for hygiene
Smooth interiors mean fewer blockages and better hygiene.
What Standards and Certifications Apply to 304 Stainless Steel Seamless Pipes?
How do you trust your pipe supplier?
Look for ASTM A312, ASTM A269, or GB/T 14976 certifications—they ensure quality and safety compliance.

Key Standards
| Standard | Purpose |
|---|---|
| ASTM A312 | Seamless and welded stainless steel pipe |
| ASTM A269 | General service tubing |
| GB/T 14976 | Stainless pipes for fluid transport |
Compliance means reliability, especially in regulated industries.
Conclusion
304 seamless pipes offer unmatched durability, hygiene, and pressure strength—making them ideal for industries that demand performance.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are stainless steel 304 seamless pipes used for?
Used in food, oil, chemical, and pharma industries for leak-free and clean fluid transport.
How are 304 stainless steel seamless pipes different from welded pipes?
Seamless pipes have no welds, making them stronger and more pressure-resistant than welded ones.
What is the chemical composition of 304 stainless steel seamless pipes?
Typically 18–20% chromium, 8–10.5% nickel, with carbon ≤ 0.08%.
What standards govern the manufacture of 304 seamless pipes?
ASTM A312, ASTM A269, and KB/T 14976 define size, strength, and composition.
Can 304 seamless pipes withstand high temperatures?
Yes, they operate safely up to ~870 °C.
What sizes and thicknesses are available for 304 seamless pipes?
Diameters range from 1/8" to 30" with wall thickness per Schedule 10, 40, 80.
Are 304 stainless steel seamless pipes corrosion resistant?
Yes, due to high chromium and nickel content.
How smooth is the surface of 304 seamless pipes?
Available in mill, 180 grit, and 320 grit finishes for different hygiene needs.
What industries commonly use 304 stainless steel seamless pipes?
Food, chemical, pharma, oil & gas, and architecture.
How do you maintain and inspect 304 stainless steel seamless pipes?
Regular cleaning and non-destructive testing like ultrasonic or radiographic inspection.
Footnotes:
-
The rotary piercing process manufactures seamless pipes by heating solid steel billets to 1250-1300°C and feeding them between two specially contoured barrel-shaped rolls rotating in the same direction with their axes inclined 3-6° to the horizontal. A water-cooled piercing plug positioned in the roll gap creates the hollow shell as the billet undergoes severe deformation, producing a thick-walled hollow tube that is then elongated and sized through subsequent rolling operations without any welding at any stage of production. ↩
-
Chromium forms a protective chromium oxide (Cr₂O₃) passive film on the stainless steel surface that is extremely thin (2-3 nanometers), self-healing when damaged, and prevents further corrosion by blocking oxygen diffusion to the underlying steel. This passive layer forms spontaneously when chromium (minimum 10.5%, with 18% in 304) reacts with oxygen in air or water, creating an invisible, tenacious barrier that gives stainless steel its characteristic corrosion resistance and makes it suitable for harsh environments. ↩
-
Austenitic stainless steel refers to the 300-series family (including 304) characterized by a face-centered cubic (FCC) crystal structure stabilized by nickel content, which makes it non-magnetic in the annealed condition, highly formable and weldable, and unable to be hardened by heat treatment (only by cold working). Type 304, containing 18% chromium and 8% nickel (often called 18/8), is the most common austenitic grade worldwide, offering excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical properties at both cryogenic and elevated temperatures. ↩
-
ASTM A312 is the standard specification for seamless, straight-seam welded, and heavily cold worked austenitic stainless steel pipes intended for high-temperature service and general corrosive environments. The specification covers chemical composition requirements (chromium, nickel, carbon limits), mechanical properties (minimum tensile and yield strength, elongation), heat treatment conditions (solution annealing at 1010-1120°C with rapid quenching), dimensional tolerances, and testing requirements including nondestructive electric tests or hydrostatic pressure tests to ensure quality and reliability. ↩
-
Sanitary surface finishes for stainless steel pipes in food, pharmaceutical, and beverage applications require interior surface roughness values of Ra ≤ 0.5-0.8 µm (20-32 microinches) to prevent bacterial adhesion and facilitate thorough cleaning. These smooth, crevice-free surfaces are achieved through mechanical polishing (180-320 grit) or electropolishing, meeting ASTM A270 and 3-A Sanitary Standards, and are essential for maintaining product purity, preventing contamination, and complying with FDA and GMP requirements in regulated industries. ↩
-
Mirror finish stainless steel surfaces are characterized by highly reflective, smooth appearances with surface roughness (Ra) values typically below 0.4-0.5 µm, achieved through fine mechanical polishing (320+ grit) or electropolishing that removes microscopic peaks and valleys. This ultra-smooth finish (#8 or BA finish) provides optimal hygiene in pharmaceutical and food processing by minimizing bacterial adhesion sites, facilitating easier cleaning and sterilization, and offering superior aesthetic appeal for architectural and high-purity applications where both performance and appearance are critical. ↩

